L'ophthalmology
is the field concerned with the affections of the eye. These diseases constitute an important part of the reasons for consultations in our clinic.
The ophthalmological examination includes an exploration of the animal's vision as well as an examination of the different structures of the eye: eyelids, conjunctiva, cornea, iris, lens, retina.
The ophthalmological consultation takes place in several stages: first with the naked eye and then using different instruments depending on the pathology observed:
- slit lamp (or bio-microscope):
Allows observation of the eyelids, cornea, anterior chamber, iris, etc.
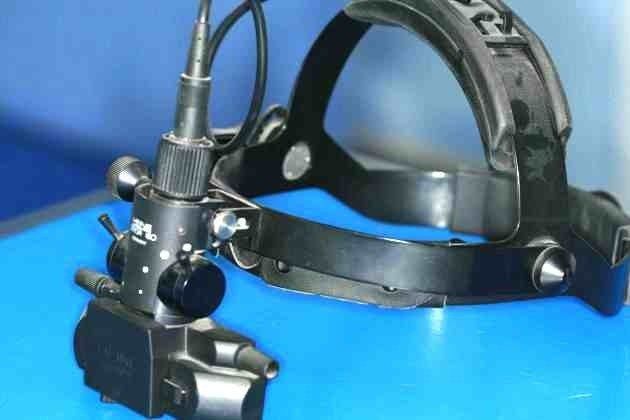
- direct and indirect ophthalmoscopes:
- tonopen:
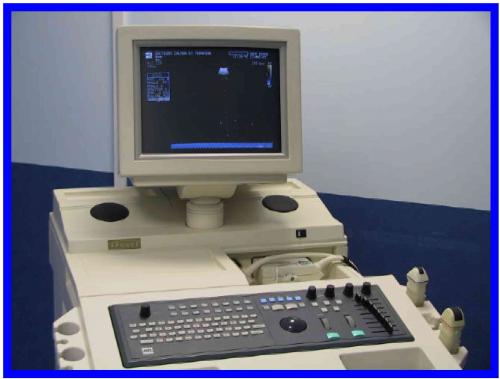
- ultrasound:
Ultrasound makes it possible to explore the various non-visible structures of the eye as well as the orbit (abscesses, cysts, tumours).
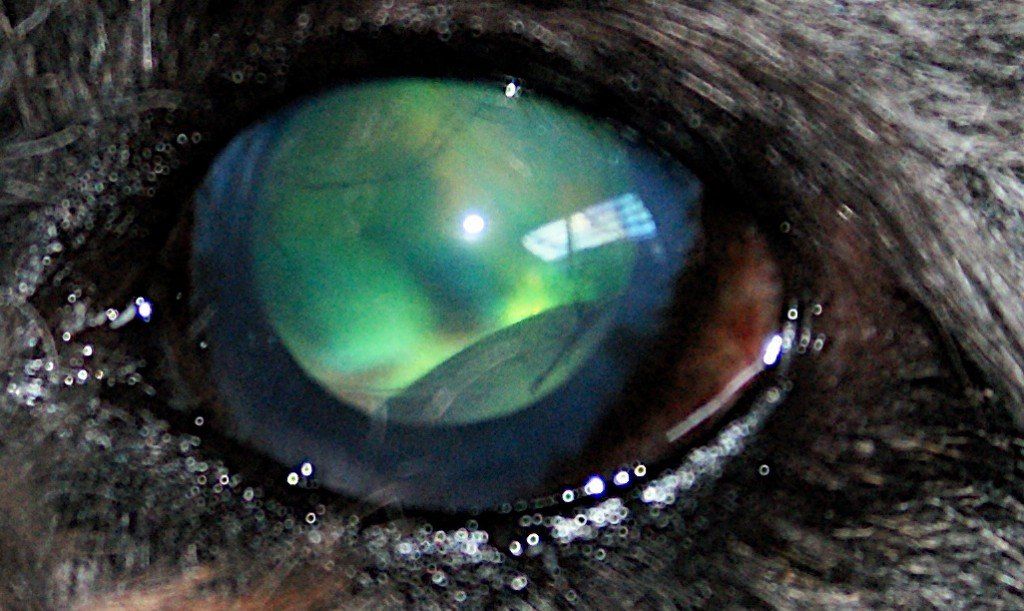
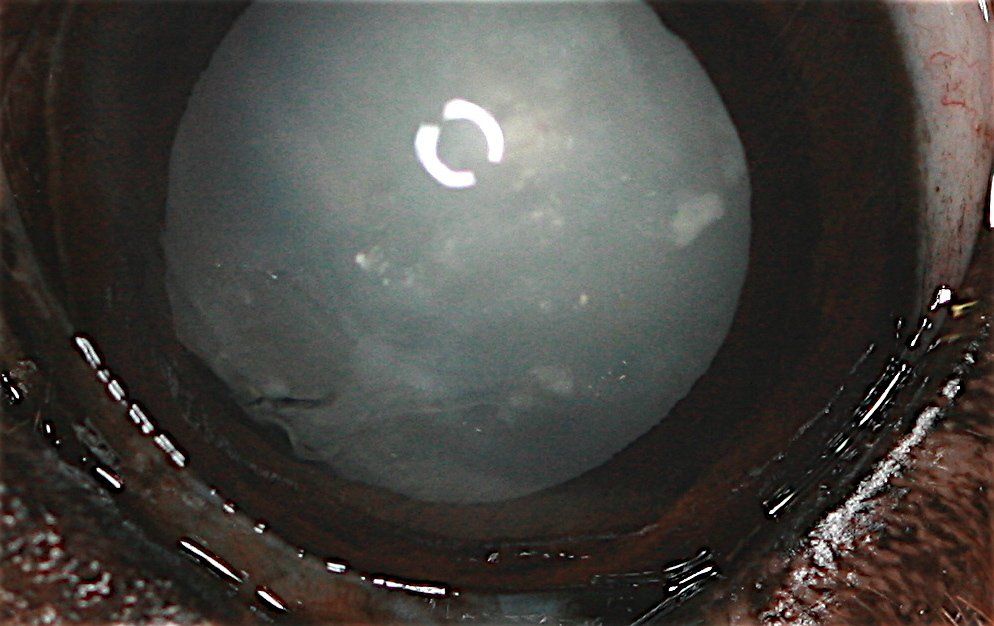
As in humans, many pathologies exist: conjunctivitis, keratitis, corneal ulcers, glaucoma, uveitis, cataracts, etc.
Most eye surgeries are performed at the clinic.
For more complex interventions (cataract surgery by phacoemulsification, treatment of glaucoma by endolaser), we work with a clinic in Blagnac (31) specializing in this type of surgery.
Some examples of clinical cases:
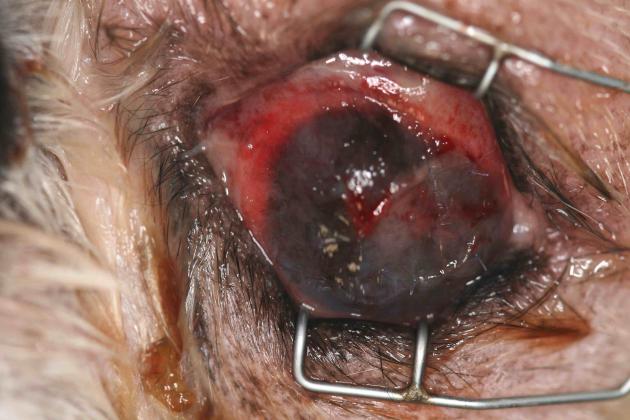
"Athos, male shih tzu, 11 years old, was presented for consultation for a corneal perforation dating back eight days following a fight with a cat. On the day of the consultation, Athos was shot (temperature 39.5°C) , no longer eating. The orbital region is very swollen, with an abscess under the palpebral and retrobulbar. The pain is intense and the ophthalmological examination is carried out under tranquilization."
Presence of a central perforation of the cornea with staphyloma, the whole being covered with a fibrin plug. Pus flows from a wound in the upper palpebral conjunctiva.
An intervention is performed under an operating microscope. The area is cleaned and disinfected. The fibrin plug is removed and reveals a staphyloma (passage of part of the iris in the corneal breach). In view of the age of the staphylop, a section of the herniated part of the iris is made. Anterior chamber flushing is performed. A viscoelastic substance Acrivet Biovisc® 1.2% is injected to restore ocular volume.
The infected appearance of the conjunctiva prevents us from performing a conjunctival flap to treat the corneal perforation.
A Vet BioSISt® prosthesis is placed and sutured using separate stitches with PDS 6/0.
A Vet BioSISt® prosthesis is placed and sutured using separate stitches with PDS 6/0.
Post-surgical treatment includes systemic antibiotic therapy and oral analgesics for 10 days. Locally, a drop of eye drops is instilled 3 times a day for 3 days.
A straitjacket is put in place.
A straitjacket is put in place.