In order to better treat your companion, the clinic offers you a new therapeutic alternative: the injection of PRP (plasma rich in platelets) associated with HA (hyaluronic acid).
PRP is a natural product derived from the centrifugation of the patient's blood. Platelets are formed elements of blood with a lifespan of 8 to 10 days. When injected into the osteoarthritis site, platelet activation releases growth factors that accelerate healing and reduce pain.
Hyaluronic acid (HA) is a chondroprotector secreted by cartilage cells and present in large quantities in healthy joints.
In an arthritic joint, the HA is degraded, its concentration drops, which leads to a reduction in the properties of lubrication and protection of the cartilage.
HA shows anti-inflammatory, analgesic effects and imparts visco-elastic and lubricating properties to joint fluid.
Intra-articular injections of hyaluronic acid (viscosupplementation) are commonly practiced in human medicine.
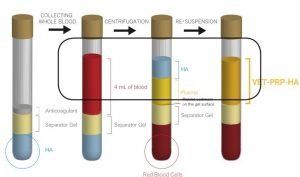
The majority of experimental studies in dogs show positive effects.Blood is taken from your pet and then centrifuged in a specialized syringe containing hyaluronic acid. Such centrifugation removes virtually all blood cells except platelets. Enriched plasma contains activated platelets, growth factors and proteins, this platelet-enriched portion is then mixed with hyaluronic acid.
The syringe containing the mixture is used directly for intra-articular injection after aseptic preparation of the joint. It can be performed 1 to 4 injections for each joint depending on the severity of the osteoarthritis.
The main indications are the prevention and postoperative treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee, elbow and shoulder and hips.
The PRP is interesting in addition to the treatment of tears of the cranial cruciate ligament.
It is also used in shoulder instability treated late with joint degradation.
The effectiveness of PRP appears similar to that of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs but it lasts well beyond the treatment. Our personal experience shows us that several injections improve the quality of clinical results and improve the quality of life of the animal suffering from osteoarthritis.
The PRP is interesting in addition to the treatment of tears of the cranial cruciate ligament.
It is also used in shoulder instability treated late with joint degradation.
The effectiveness of PRP appears similar to that of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs but it lasts well beyond the treatment. Our personal experience shows us that several injections improve the quality of clinical results and improve the quality of life of the animal suffering from osteoarthritis.